VITAMIN D and CANCER - a quick review and a look at new research (4 papers reviewed)
With the recent explosion of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Induced Turbo Cancers in young people, there is an intense interest in cancer prevention and cancer treatment.
Vitamin D had a tremendous impact on the COVID-19 pandemic. It was attacked by Public Health Officials, who were more interested in driving up COVID-19 deaths, than preventing them.
What about Vitamin D and Cancer?
I review 4 recent papers that look at a large body of literature regarding Vitamin D and Cancer
Some highlights:
July 2023 (Seraphin et al) - The impact of vitamin D on cancer: A mini review
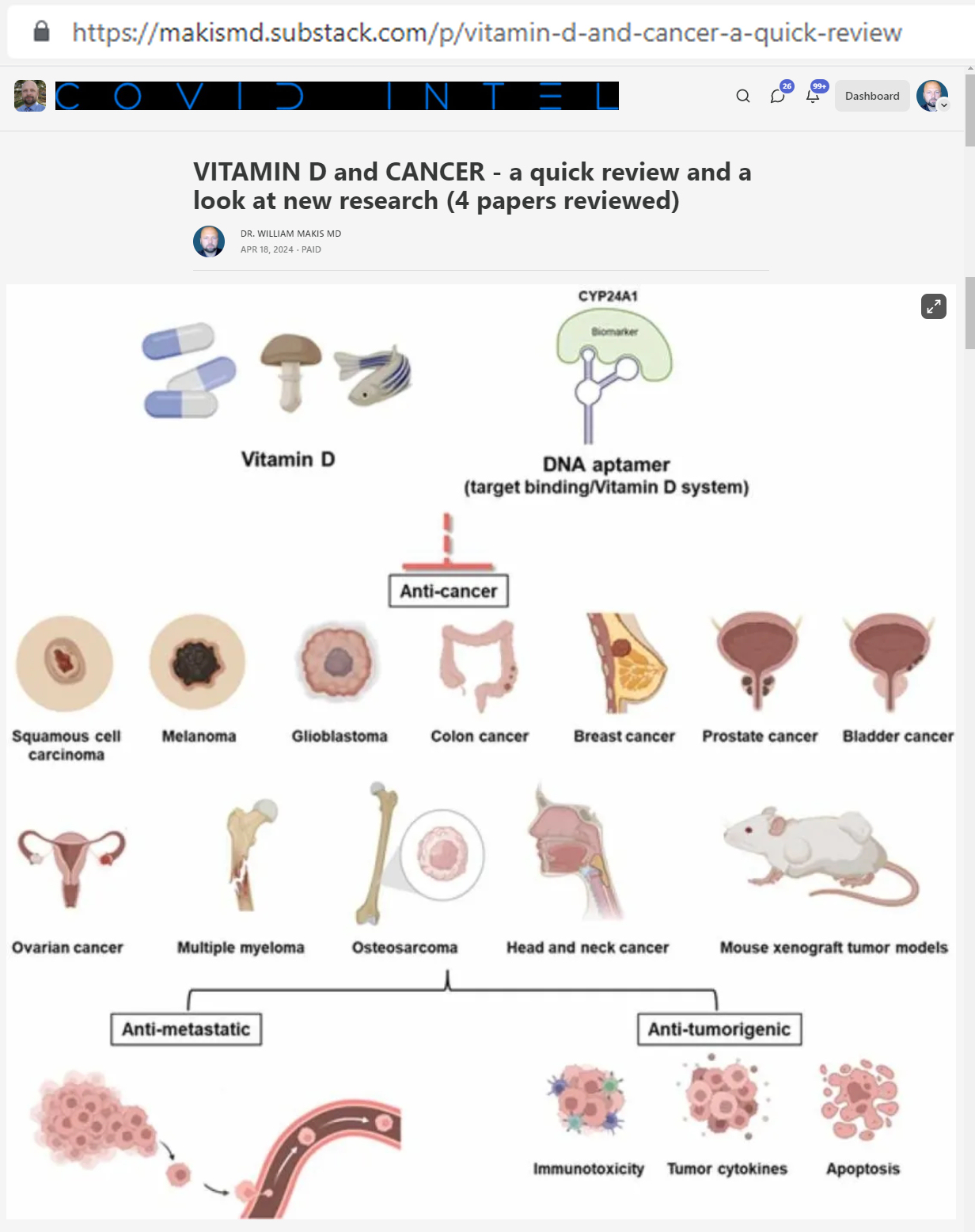
"Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to the development and progression of a number of cancer types"
"Vitamin D continues to show positive anti-cancer effects against many types of cancer."
"Recent epigenomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic studies have revealed novel vitamin D-mediated biological mechanisms that regulate cancer cell self-renewal, differentiation, proliferation, transformation, and death"
Breast cancer - Vitamin D deficiency is very common in breast cancer patients, deficiency is linked to higher grade of breast cancer and ER- subtypes
Ovarian cancer - people with high Vitamin D levels had 37% lower risk of developing ovarian cancer
Glioblastoma - Vitamin D induced apoptosis, cytotoxic autophagy and inhibited migration and invasiveness, and cancer stemness
Colorectal cancer - Higher Vitamin D intake resulted in 17% lower risk of colorectal cancer, suppresses colorectal cancer stem cells
Prostate cancer - Vitamin D can inhibit tumor progression by negatively regulating androgen receptor signalling.
Melanoma - people on Vitamin D supplements had lower risk of melanoma, low Vitamin D levels associated with reduced melanoma patient survival
March 2023 - Nemeth et al - Interplay of Vitamin D and SIRT1 in Tissue-Specific Metabolism—Potential Roles in Prevention and Treatment of Non-Communicable Diseases Including Cancer
"Prospective and retrospective epidemiological studies reported an association between a 25(OH)D3 level below 20 ng/mL and a 30–50% increased risk of colon, prostate, and breast cancer and higher mortality"
I’m often asked by COVID-19 mRNA Vaccinated individuals how to either prevent cancer from developing or once diagnosed, how to best treat a Turbo Cancer, given that Oncologists have no idea how to deal with this new vaccine induced phenomenon.
Ivermectin and Fenbendazole (or Mebendazole) have emerged as leading options for an alternative treatment approach to mRNA Induced Turbo Cancers, however, a comprehensive treatment plan will involve several other elements.
One of these is Vitamin D.
Supplementing Vitamin D is easy and cheap.
And it seems big pharma really doesn't want Vitamin D to get any traction in cancer prevention and cancer treatment.
However, there is substantial evidence to suggest that with daily Vitamin D supplementation you can achieve:
-> 10-30% decrease in the risk of getting certain cancers such as breast, ovarian, lung, colorectal, prostate, melanoma
-> 10-30% decrease in cancer mortality once diagnosed.
These are substantial benefits that should not be ignored.